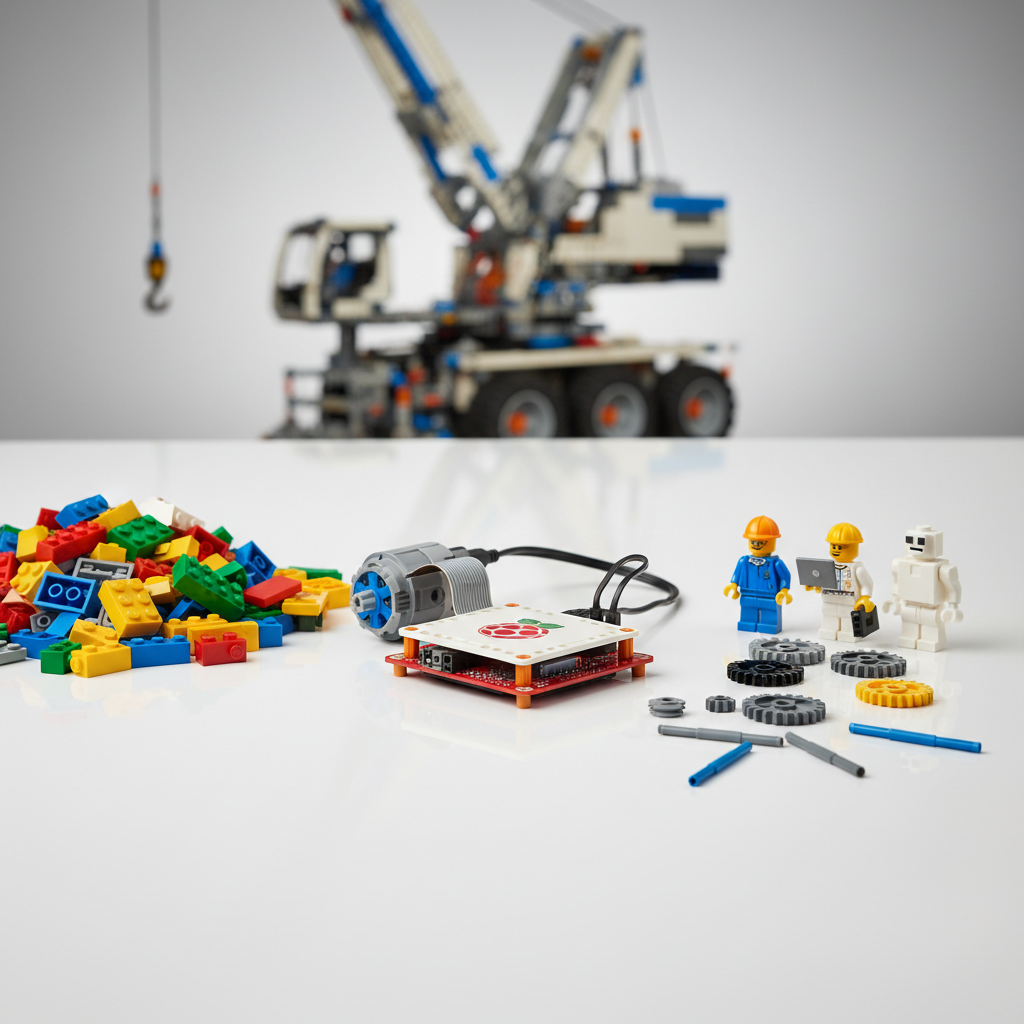
The Raspberry Pi Build HAT is a game-changer for LEGO robotics. This add-on board connects to the Pi's 40-pin GPIO header and provides four LPF2 ports, natively accepting LEGO Technic, SPIKE, and MINDSTORMS motors and sensors. This guide covers everything from installation to advanced Python integration.
Table of Contents
Hardware Overview
The Build HAT solves the biggest challenge in Pi + LEGO integration: power and voltage management.
Key Specifications
| Feature |
Specification |
| LPF2 Ports |
4 ports (A, B, C, D) - fewer than SPIKE Prime's 6 |
| Onboard MCU |
Raspberry Pi RP2040 for low-level motor control |
| Motor Voltage |
~7.2V via dedicated driver IC per port |
| Logic Voltage |
3.3V always present on LPF2 connector |
| Power Input |
7.2-8.5V DC barrel jack (official PSU: 8V) |
| Communication |
115200 baud serial (8N1) to Pi |
| Compatibility |
All Pi with 40-pin GPIO: Pi 5, Pi 4, Pi 3, Pi Zero 2 W |
💡 Key Insight: The onboard RP2040 handles all the timing-critical motor control, freeing your Pi's CPU for high-level Python code, computer vision, or web servers.
Compatible LEGO Devices
-
Motors: Technic Large/XL, SPIKE Prime Medium/Large, MINDSTORMS motors
-
Sensors: Color sensor, Distance sensor, Force sensor
-
Not Compatible: Powered Up hub (it IS a hub), Power Functions (different connector)
Installation & Setup
Hardware Setup
- Power off your Raspberry Pi
- Align the Build HAT with the 40-pin GPIO header
- Press down firmly until fully seated
- Connect 8V power supply to the barrel jack
- Connect motors/sensors to the LPF2 ports (A, B, C, D)
⚠️ Power Note: The Build HAT can power both the Pi and LEGO motors from its barrel jack. You don't need a separate USB power supply for the Pi when using the Build HAT.
Software Installation
# Update your Pi
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
# Enable serial port (required for Build HAT communication)
sudo raspi-config nonint do_serial 2 # Enable serial, disable console
# Install the Build HAT Python library
pip3 install buildhat
# Verify installation
python3 -c "from buildhat import Hat; hat = Hat(); print(f'Build HAT firmware: {hat.get_firmware()}')"
# Reboot to apply serial changes
sudo reboot
⚠️ API Note: The Build HAT Python library is under active development. Some methods may change between versions. Current stable version on
PyPI is recommended.
Motor Control
Basic Motor Operations
from buildhat import Motor
# Initialize motor on port A
motor = Motor('A')
# Run at speed (degrees per second)
motor.run_for_seconds(2, speed=50) # Run for 2 seconds at 50% speed
# Run for specific rotations
motor.run_for_rotations(3, speed=75) # 3 full rotations at 75%
# Run to absolute position
motor.run_to_position(180, speed=50) # Move to 180 degrees
# Get current position
position = motor.get_position()
print(f"Motor position: {position} degrees")
Motor Pair for Drive Systems
from buildhat import MotorPair
# Initialize paired motors for tank drive
motors = MotorPair('A', 'B')
# Move forward
motors.run_for_seconds(2, speedl=50, speedr=50)
# Turn left (right motor faster)
motors.run_for_seconds(1, speedl=20, speedr=50)
# Spin in place
motors.run_for_seconds(1, speedl=50, speedr=-50)
Precise Position Control
from buildhat import Motor
import time
motor = Motor('A')
# Enable position tracking
motor.set_default_speed(30)
# Move to specific angles
for angle in [0, 90, 180, 270, 360]:
motor.run_to_position(angle)
print(f"Moved to {angle}°")
time.sleep(0.5)
Sensor Reading
Color Sensor
from buildhat import ColorSensor
sensor = ColorSensor('C')
# Get detected color name
color = sensor.get_color()
print(f"Detected: {color}") # 'red', 'blue', 'green', etc.
# Get RGB values
r, g, b = sensor.get_color_rgbi()[:3]
print(f"RGB: ({r}, {g}, {b})")
# Get reflected light intensity (0-100)
light = sensor.get_reflected_light()
print(f"Reflected light: {light}%")
# Get ambient light
ambient = sensor.get_ambient_light()
print(f"Ambient light: {ambient}%")
Distance Sensor
from buildhat import DistanceSensor
sensor = DistanceSensor('D')
# Get distance in centimeters
distance = sensor.get_distance()
print(f"Distance: {distance} cm")
# Continuous monitoring
while True:
d = sensor.get_distance()
if d and d < 10:
print("Object detected nearby!")
time.sleep(0.1)
Force Sensor
from buildhat import ForceSensor
sensor = ForceSensor('B')
# Get force in Newtons (0-10N)
force = sensor.get_force()
print(f"Force: {force}N")
# Check if pressed
if sensor.is_pressed():
print("Button pressed!")
Advanced: NumPy & OpenCV Integration
The Build HAT's Python library opens the door to the entire Python ecosystem. Here's where things get powerful.
Data Logging with Pandas
from buildhat import Motor, ColorSensor
import pandas as pd
import time
motor = Motor('A')
sensor = ColorSensor('C')
# Collect data while motor runs
data = []
motor.start(speed=30)
for i in range(100):
data.append({
'time': time.time(),
'position': motor.get_position(),
'color': sensor.get_color(),
'light': sensor.get_reflected_light()
})
time.sleep(0.1)
motor.stop()
# Create DataFrame and analyze
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.to_csv('motor_data.csv')
print(df.describe())
Computer Vision with OpenCV
from buildhat import Motor
import cv2
import numpy as np
# Initialize camera and motor
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
sorting_motor = Motor('A')
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# Convert to HSV for color detection
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# Define red color range
lower_red = np.array([0, 100, 100])
upper_red = np.array([10, 255, 255])
mask = cv2.threshold(hsv, lower_red, upper_red)
# If red detected, activate sorting gate
if cv2.countNonZero(mask) > 1000:
sorting_motor.run_to_position(90) # Open gate
else:
sorting_motor.run_to_position(0) # Close gate
cv2.imshow('Frame', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
Scientific Computing with NumPy
from buildhat import Motor
import numpy as np
motor = Motor('A')
# Generate smooth acceleration curve using NumPy
speeds = np.linspace(0, 100, 50) # 0 to 100 in 50 steps
# Acceleration phase
for speed in speeds:
motor.start(speed=int(speed))
time.sleep(0.05)
# Deceleration phase
for speed in reversed(speeds):
motor.start(speed=int(speed))
time.sleep(0.05)
motor.stop()
Project Ideas
1. Data-Logging Weather Station
Use external I2C sensors (temperature, humidity, pressure) with motor-actuated displays showing current conditions.
2. Automated LEGO Sorter
Combine Pi Camera + OpenCV for part identification with Build HAT motors for conveyor and sorting gates.
3. Robotic Arm with Inverse Kinematics
Use NumPy/SciPy to calculate joint angles for precise end-effector positioning.
4. Line-Following Robot
Color sensor reads track, PID algorithm (implemented in Python) controls motor speeds for smooth following.
Resources