Smart LEGO Train Network: ESP32, RFID, and MQTT Automation
Supporting Free Content
When you purchase through our links, we earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. As an Amazon Associate and eBay Partner, this helps us keep bringing you expert LEGO® reviews and guides. Thank you for your support!
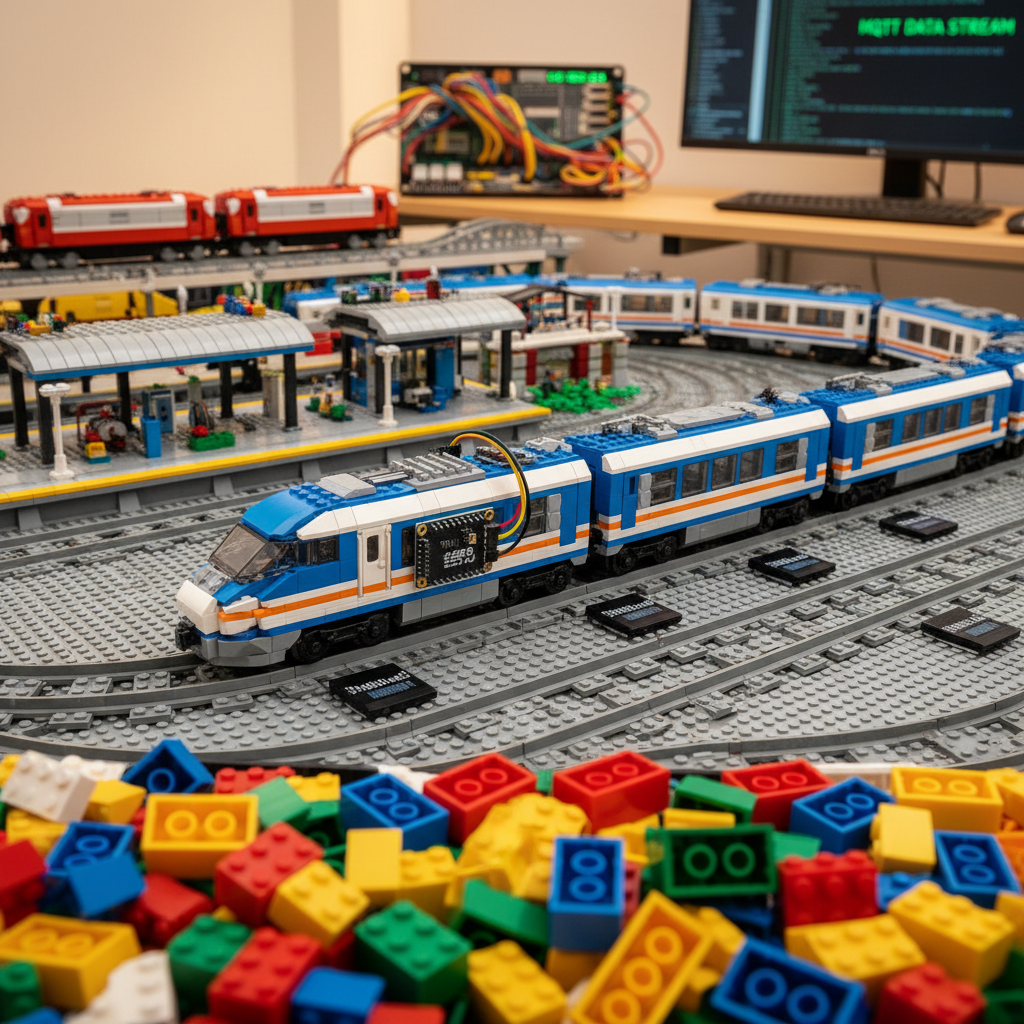
Transform your LEGO train layout from a simple loop into a fully automated transit system. Trains automatically stop at stations, obey traffic signals, and avoid collisions—all without a smartphone app. This guide covers RFID position tracking, MQTT communication, and multi-train coordination.
Table of Contents
- System Architecture
- RFID Position Tracking
- MQTT Communication
- Train-Side ESP32
- Server-Side Logic
- Home Assistant Integration
System Architecture
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ LEGO TRAIN LAYOUT │
│ │
│ [RFID Tag A] [RFID Tag B] [RFID Tag C] │
│ ║ ║ ║ │
│ ════╬════════════════════╬════════════════════╬════ │
│ ║ ║ ║ │
│ [Reader A] [Reader B] [Reader C] │
│ │ │ │ │
│ └────────────────────┴────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ [Raspberry Pi] │
│ MQTT Broker + │
│ Control Logic │
│ │ │
│ [Home WiFi] │
│ │ │
│ ┌───────────────────────┼───────────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ [Train 1] [Train 2] [Train 3] │
│ ESP32 + BLE ESP32 + BLE ESP32 + BLE │
│ → Powered Up Hub → Powered Up Hub → Powered Up │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Components
- Trackside: RFID readers (RC522) under track at key locations
- Trains: ESP32 (M5Atom) in locomotive, connects to Powered Up hub via BLE
- Server: Raspberry Pi running Mosquitto MQTT broker
- Communication: WiFi for MQTT, BLE for hub control
RFID Position Tracking
Hardware: RC522 RFID Reader
- Frequency: 13.56 MHz (MIFARE)
- Read Distance: Up to 50mm (through LEGO plastic)
- Interface: SPI
- Cost: ~$3 per reader
Mounting Strategy
Side View:
┌─────┐
Track ══════════│Train│══════════
└──┬──┘
│ RFID Tag (under train)
═══════════════════════════════════ ← Track ties
│
[RC522] ← Reader under track
│
[ESP32] ← Trackside controllerReading RFID at Speed
The challenge: trains move fast, and RFID reads take time. Solutions:
- Fast polling: Read every 50ms (20 reads/second)
- Large tags: Use credit-card sized tags for longer read window
- Multiple tags: Place 2-3 tags in sequence for redundancy
Trackside ESP32 Code
#include <SPI.h>
#include <MFRC522.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
#define RST_PIN 22
#define SS_PIN 21
MFRC522 rfid(SS_PIN, RST_PIN);
WiFiClient espClient;
PubSubClient mqtt(espClient);
const char* LOCATION = "STATION_A";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
SPI.begin();
rfid.PCD_Init();
WiFi.begin("YourSSID", "YourPassword");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) delay(500);
mqtt.setServer("192.168.1.100", 1883);
}
void loop() {
mqtt.loop();
// Check for RFID tag
if (rfid.PICC_IsNewCardPresent() && rfid.PICC_ReadCardSerial()) {
// Get tag ID
String tagID = "";
for (byte i = 0; i < rfid.uid.size; i++) {
tagID += String(rfid.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
}
// Publish detection
String topic = "track/location/" + String(LOCATION);
mqtt.publish(topic.c_str(), tagID.c_str());
Serial.println("Tag detected: " + tagID + " at " + LOCATION);
rfid.PICC_HaltA();
delay(100); // Debounce
}
}
MQTT Communication
Topic Structure
track/location/{location} → Tag ID detected at location
train/{id}/location → Train's current location
train/{id}/speed → Train's current speed
train/{id}/command → Commands TO train (set speed, stop)
system/schedule → Schedule updates
system/emergency → Emergency stop all trainsMessage Flow Example
1. Trackside reader detects tag "A1B2C3" at STATION_A
→ Publish: track/location/STATION_A = "A1B2C3"
2. Server looks up tag "A1B2C3" = Train #1
→ Publish: train/1/location = "STATION_A"
3. Server checks schedule: Train #1 should stop here
→ Publish: train/1/command = "STOP"
4. Train #1 receives command, stops motor
→ Publish: train/1/speed = 0
5. After 30 seconds, server sends depart command
→ Publish: train/1/command = "SPEED:50"Setting Up Mosquitto (Raspberry Pi)
# Install Mosquitto MQTT broker
sudo apt install mosquitto mosquitto-clients
# Start broker
sudo systemctl enable mosquitto
sudo systemctl start mosquitto
# Test from command line
mosquitto_sub -t "train/#" -v # Subscribe to all train topics
mosquitto_pub -t "train/1/command" -m "STOP" # Send commandTrain-Side ESP32 Code
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
#include "Lpf2Hub.h"
Lpf2Hub trainHub;
WiFiClient espClient;
PubSubClient mqtt(espClient);
const char* TRAIN_ID = "1";
int currentSpeed = 0;
void mqttCallback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length) {
String message = "";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
message += (char)payload[i];
}
Serial.println("Received: " + String(topic) + " = " + message);
if (String(topic).endsWith("/command")) {
if (message == "STOP") {
setSpeed(0);
} else if (message.startsWith("SPEED:")) {
int speed = message.substring(6).toInt();
setSpeed(speed);
}
}
}
void setSpeed(int speed) {
currentSpeed = speed;
if (trainHub.isConnected()) {
trainHub.setBasicMotorSpeed((byte)PoweredUpHubPort::A, speed);
}
// Publish new speed
String topic = "train/" + String(TRAIN_ID) + "/speed";
mqtt.publish(topic.c_str(), String(speed).c_str());
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Connect WiFi
WiFi.begin("YourSSID", "YourPassword");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) delay(500);
// Setup MQTT
mqtt.setServer("192.168.1.100", 1883);
mqtt.setCallback(mqttCallback);
// Subscribe to commands
String cmdTopic = "train/" + String(TRAIN_ID) + "/command";
mqtt.subscribe(cmdTopic.c_str());
mqtt.subscribe("system/emergency");
// Initialize LEGO hub connection
trainHub.init();
}
void loop() {
mqtt.loop();
// Maintain hub connection
if (trainHub.isConnecting()) {
trainHub.connectHub();
}
delay(10);
}
Server-Side Logic (Python)
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
import json
import time
from datetime import datetime
# Train state tracking
trains = {}
schedule = {
"STATION_A": {"stop_duration": 30},
"STATION_B": {"stop_duration": 20},
"SIGNAL_1": {"check_collision": True}
}
# Tag to train mapping
tag_to_train = {
"a1b2c3d4": "1",
"e5f6g7h8": "2",
}
def on_message(client, userdata, msg):
topic = msg.topic
payload = msg.payload.decode()
if topic.startswith("track/location/"):
location = topic.split("/")[-1]
tag_id = payload.lower()
if tag_id in tag_to_train:
train_id = tag_to_train[tag_id]
handle_train_arrival(client, train_id, location)
def handle_train_arrival(client, train_id, location):
print(f"Train {train_id} arrived at {location}")
# Update train location
trains[train_id] = {"location": location, "time": time.time()}
client.publish(f"train/{train_id}/location", location)
# Check schedule
if location in schedule:
loc_config = schedule[location]
if "stop_duration" in loc_config:
# Stop train
client.publish(f"train/{train_id}/command", "STOP")
print(f"Train {train_id} stopping for {loc_config['stop_duration']}s")
# Schedule departure (in real system, use threading or asyncio)
time.sleep(loc_config['stop_duration'])
client.publish(f"train/{train_id}/command", "SPEED:50")
if loc_config.get("check_collision"):
# Check if another train is in the next block
# Implement block signaling logic here
pass
# Setup MQTT client
client = mqtt.Client()
client.on_message = on_message
client.connect("localhost", 1883)
client.subscribe("track/location/#")
print("Train control server running...")
client.loop_forever()
Home Assistant Integration
Expose your train system to Home Assistant for voice control and automation.
configuration.yaml
mqtt:
sensor:
- name: "Train 1 Location"
state_topic: "train/1/location"
- name: "Train 1 Speed"
state_topic: "train/1/speed"
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- name: "Train 2 Location"
state_topic: "train/2/location"
button:
- name: "Start Train 1"
command_topic: "train/1/command"
payload_press: "SPEED:50"
- name: "Stop Train 1"
command_topic: "train/1/command"
payload_press: "STOP"
- name: "Emergency Stop All"
command_topic: "system/emergency"
payload_press: "STOP"
Automation: Start Trains at Opening Time
automation:
- alias: "Start trains at 9 AM"
trigger:
- platform: time
at: "09:00:00"
action:
- service: mqtt.publish
data:
topic: "train/1/command"
payload: "SPEED:40"
- delay: "00:00:05"
- service: mqtt.publish
data:
topic: "train/2/command"
payload: "SPEED:40"
Voice Control
With Home Assistant exposed to Alexa or Google Assistant:
- "Alexa, turn on Start Train 1"
- "Hey Google, activate Emergency Stop All"
Bill of Materials
| Component | Quantity | ~Cost |
|---|---|---|
| ESP32 (M5Atom or similar) | 1 per train + 1 per station | $8 each |
| RC522 RFID Reader | 1 per detection point | $3 each |
| RFID Tags (MIFARE) | 1 per train | $0.50 each |
| Raspberry Pi (MQTT server) | 1 | $35-55 |
| LEGO Powered Up Hub | 1 per train | Included with train sets |
Use Our Tools to Go Further
Get more insights about the sets mentioned in this article with our free LEGO tools